
Mega Doctor News
By Chloe Corey, Mayo Clinic News Network
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: I’ve recently been diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease. I’m trying to understand what IBD is and how it will affect me. Will I need surgery?
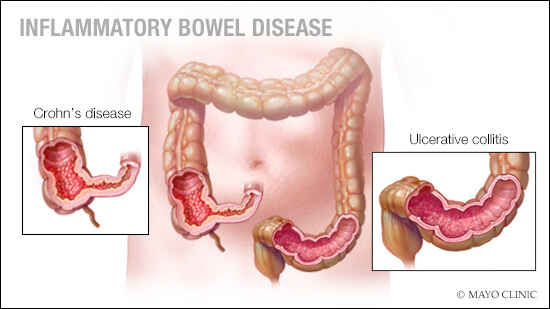
ANSWER: Inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, is an umbrella term for a group of chronic conditions that cause inflammation and swelling in the digestive tract. It primarily includes two conditions: ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. While both involve inflammation, they affect different parts of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and behave differently over time.
Symptoms of both categories of IBD usually include belly pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, extreme fatigue colitis typically affects the colon and rectum, and it leads to the development of sores called ulcers. On the other hand, Crohn’s disease primarily affects the small intestine and often involves deeper and weight loss. Some people experience mild illness, while in others, the disease can be debilitating and lead to life-threatening complications.
Diagnosing IBD
Diagnosing IBD involves a combination of tests and procedures. Your care team will begin by taking a detailed medical history and asking about your symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis, your care team may recommend:
- Blood tests to check for signs of inflammation, anemia or infection.
- Stool studies to rule out infections and detect markers of inflammation.
- Endoscopic procedures, such as:
- Colonoscopy, which allows doctors to view the entire colon and take biopsies.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy, used when the colon is too inflamed for a complete colonoscopy.
- Upper endoscopy, if symptoms involve the upper GI tract.
- Capsule endoscopy, where you swallow a small camera to examine the small intestine.
- Balloon-assisted enteroscopy, which is used to explore deeper parts of the small bowel.
A biopsy, a small tissue sample taken during endoscopy, is essential to confirm the diagnosis and distinguish IBD from other causes of inflammation.
Understanding the role of surgery
Most people with IBD are treated first with medications. These include anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors and biologics that target specific pathways in the immune response. However, surgery can become necessary when medications are no longer effective, not well tolerated or when complications arise.
In ulcerative colitis, a colectomy is performed when medications fail or when complications like perforation, obstruction, or cancerous changes occur. A colectomy is when the surgeon removes the entire colon and rectum. An internal pouch is then made and surgically attached to the anus to allow passing waste without an external bag. Sometimes, an internal pouch isn’t possible. In these cases, a permanent opening is surgically created in the abdomen, called an ileostomy.
Up to two-thirds of people with Crohn’s disease will require at least one surgery in their lifetime. During this operation, the surgeon removes the damaged part of the digestive tract and reconnects the healthy sections. Surgeons aim to preserve as much of the healthy intestine as possible. Surgery also may be needed for issues such as fistulas, bowel obstructions or perforations.
Surgical decisions are highly individualized and should be made in collaboration between the patient, gastroenterologist and surgeon. Factors that influence the decision include:
- Severity and location of disease.
- Response to medications.
- Overall health and nutritional status.
- Quality of life and personal preferences.
In urgent situations, such as a perforated bowel or severe bleeding, surgery may be performed immediately. But in most cases, there’s time for thoughtful discussion and planning.
What to expect moving forward
If you’re facing surgery for IBD, know that you’re not alone — and you’re not without options. The goal of surgery is always to improve your quality of life, reduce symptoms and prevent complications. Seek care from centers like Mayo Clinic that are well versed in IBD treatment and that approach care in a collaborative, compassionate way, tailoring the treatment plan to your unique needs.
Patients should feel empowered to ask questions and be part of the decision-making process. When surgery isn’t urgent, your team will work with you to ensure you’re in the best possible health before the operation and choose the approach to support long-term success.
Kellie Mathis, M.D., Colon and Rectal Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota








