Combating Coronavirus has been Containment, Mitigation, Testing, Developing Treatments and Vaccines
By Roberto Hugo Gonzalez
As originally published by Mega Doctor News newsprint April 2020
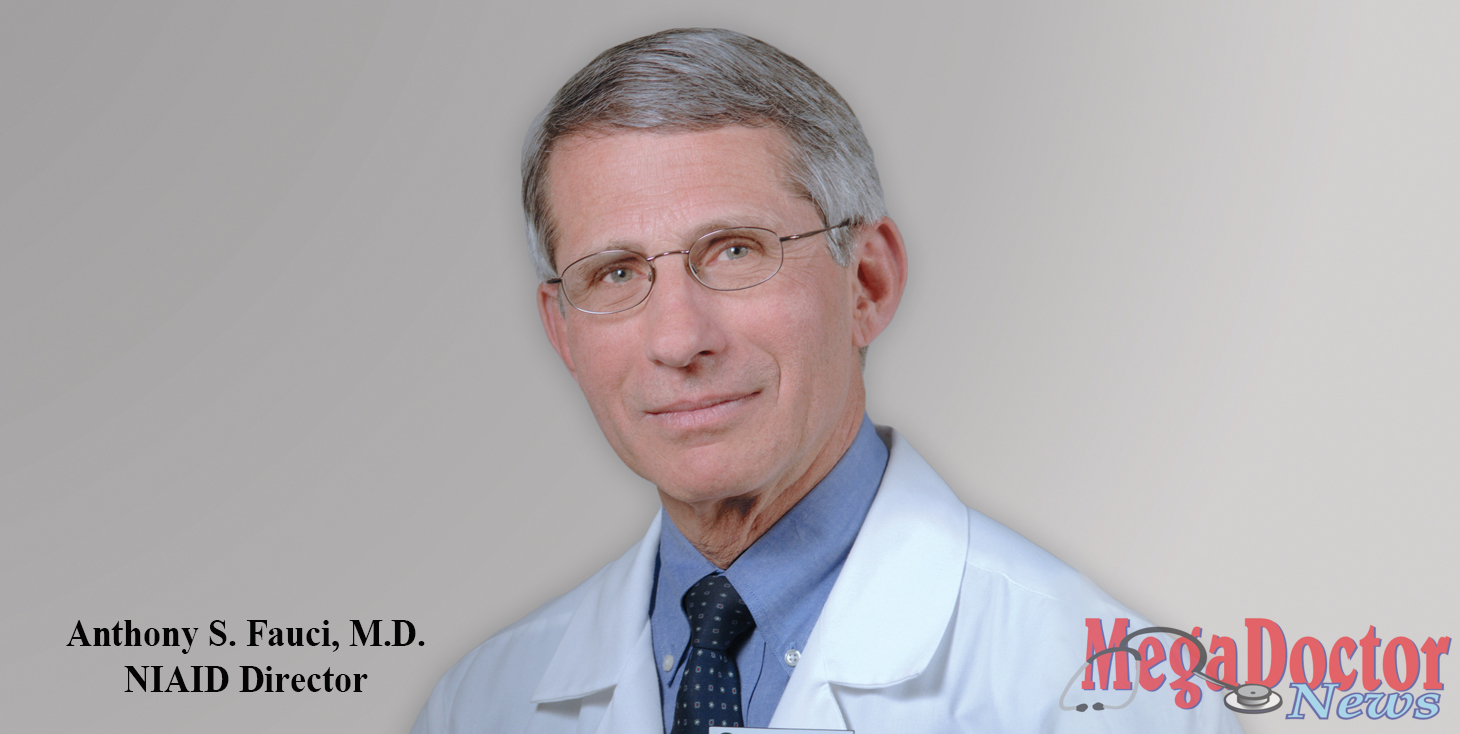
Every time I heard Dr. Anthony S. Fauci speak to explain the intricacies of infectious diseases, the more I got interested in knowing about this man who seemed to know all the answers. He was appointed director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) in 1984.
Dr. Tony, as they call him, has advised six U.S. presidents on HIV/AIDS and many other domestic and global health issues. He was one of the principal architects of the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), a program that has saved millions of lives throughout the developing world.
As the world grapples with the Coronavirus immunology, Dr. Anthony Fauci has once again become a public force who translates complex medical information into everyday language.
Fauci is one of the key advisors to President Donald Trump at the White House and the Department of Health and Human Services on the virus and how to combat it. He said, during one the interviews, that if we do not successfully prevent infections from coming in and deal with the ones we have, it could get as bad as Italy.
He said, “For a while, life is not going to be the way it used to be in the United States. We want to do what’s best for the American public.” What he said sounded easy, but it is not. People have already begun to protest in multiple states demanding that the government open the country for business. Those in the know, believe that we should wait until is safe. They want to save lives.
Dr. Fauci has acquired so much experience that his approach is something that he learned through the years. To combat the Coronavirus he started with containment, mitigation, and the increase in testing aside from the development of treatments and vaccines.
During one of the many television interviews, he pointed out, “I believe to have the agent in hand, that the amount of effort and energy that’s being put into it by biomedical sciences, that within a reasonable period of time, we’ll have a lot of these answers.”
On unique moment in the history of the Coronavirus was when President Donald Trump said, “I said earlier today that I hope we can do this by Easter.”
To that, Dr. Fauci said, “You don’t make the timeline. The virus makes the timeline.”
There is no doubt, the coronavirus has become an all-consuming crisis for the White House, the United States, and the rest of the world. It has also crushed the U.S. economy, eliminating thousands of businesses and creating massive layoffs.

The following is a redacted list showing a timeline of how COVID-19 has spread across the United States and how President Trump and the White House have responded.
December 31: China reports the discovery of the coronavirus to the World Health Organization.
January 3: CDC Director Robert Redfield sent an email to the director of the Chinese CDC, George Gao, formally offering to send U.S. experts to China to investigate the coronavirus.
January 5: CDC Director Redfield sent another email to the Chinese CDC Director, George Gao, formally offering to send U.S. experts to China to investigate the coronavirus outbreak.
January 6: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a level I travel notice for Wuhan, China due to the spreading coronavirus.
January 7: The CDC established a coronavirus incident management system to better share and respond to information about the virus.
January 17: The CDC began implementing public health entry screening at the 3 U.S. airports that received the most travelers from Wuhan – San Francisco, New York JFK, and Los Angeles.
January 20: Dr. Fauci announces the National Institutes of Health is already working on the development of a vaccine for the coronavirus.
January 21: The CDC activated its emergency operations center to provide ongoing support to the coronavirus response.
January 23: The CDC sought a “special emergency authorization” from the FDA to allow states to use its newly developed coronavirus test.
January 27: The CDC issued a level III travel health notice urging Americans to avoid all nonessential travel to China due to the coronavirus.
January 27: The White House Coronavirus Task Force started meeting to help monitor and contain the spread of the virus and provide updates to the President.
January 31: The Trump Administration: Declared the coronavirus a public health emergency. Announced Chinese travel restrictions. Suspended entry into the United States for foreign nationals who pose a risk of transmitting the coronavirus.
January 31: The Department of Homeland Security took critical steps to funnel all flights from China into just 7 domestic U.S. airports.
February 3: The CDC had a team ready to travel to China to obtain critical information on the novel coronavirus but were in the U.S. awaiting permission to enter by the Chinese government.
February 2: The CDC expanded enhanced entry screening to eight major airports across the nation.
February 4: President Trump vowed in his State of the Union Address to “take all necessary steps” to protect Americans from the coronavirus.
February 6: The CDC began shipping CDC-Developed test kits for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus to U.S. and international labs.
February 11: The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) expanded a partnership with Janssen Research & Development to “expedite the development” of a coronavirus vaccine.
February 12: The U.S. shipped test kits for the 2019 novel coronavirus to approximately 30 countries who lacked the necessary reagents and other materials.
February 14: The CDC began working with five labs to conduct “community-based influenza surveillance” to study and detect the spread of coronavirus.
February 18: HHS announced it would engage with Sanofi Pasteur in an effort to quickly develop a coronavirus vaccine and to develop treatment for coronavirus infections.
February 22: A WHO team of international experts arrives in Wuhan, China.
February 24: The Trump Administration sent a letter to Congress requesting at least $2.5 billion to help combat the spread of the coronavirus.
February 26: President Trump discussed coronavirus containment efforts with Indian PM Modi and updated the press on his Administration’s containment efforts in the U.S. during his state visit to India.
February 29: The Trump Administration: Announced a level 4 travel advisory to areas of Italy and South Korea. Barred all travel to Iran. Barred the entry of foreign citizens who visited Iran in the last 14 days.
March 3: The White House announced President Trump donated his fourth quarter salary to fight the coronavirus.
March 4: The Trump Administration announced the purchase of approximately 500 million N95 respirators over the next 18 months to respond to the outbreak of the novel coronavirus.
March 6: President Trump signed an $8.3 billion bill to fight the coronavirus outbreak.
The bill provides $7.76 billion to federal, state, & local agencies to combat the coronavirus and authorizes an additional $500 million in waivers for Medicare telehealth restrictions.
March 11: President Trump: Announced travel restrictions on foreigners who had visited Europe in the last 14 days; Directed the SBA to issue low-interest loans to affected small businesses and called on congress to increase this fund by $50 billion; Directed the Treasury Department to defer tax payments for affected individuals & businesses and to provide $200 billion in “additional liquidity”; Met with American bankers at the White House to discuss coronavirus.
March 13: President Trump declared a national emergency in order to access $42 billion in existing funds to combat the coronavirus.
March 13: President Trump announced: Public-private partnerships to open up drive-through testing collection sites; A pause on interest payments on federal student loans; An order to the Department of Energy to purchase oil for the strategic petroleum reserve.
March 14: The Coronavirus Relief Bill passed the House of Representatives.
March 15: All 50 states were contacted through FEMA to coordinate “federally-supported, state-led efforts” to end coronavirus.
March 16: President Trump announced “15 days to slow the spread” coronavirus guidance.
March 17: President Trump announced: CMS will expand telehealth benefits for Medicare beneficiaries; Relevant Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act penalties will not be enforced; The Army Corps of Engineers is on “standby” to assist federal & state governments.
March 17: President Trump spoke to fast food executives from Wendy’s, McDonald’s, and Burger King to discuss drive-thru services recommended by CDC.
March 17: Secretary of Agriculture Sonny Perdue announced a partnership between USDA, Baylor University, McLane Global, and Pepsi Co. to provide one million meals per weak to rural children in response to widespread school closures.
March 17: The Treasury Department: Contributed $10 billion through the economic stabilization fund to the Federal Reserve’s commercial paper funding facility.
Deferred $300 billion in tax payments for 90 days without penalty, up to $1 million for individuals & $10 million for business.
March 18: President Trump signed the Families First Coronavirus Response Act, which provides free testing and paid sick leave for workers impacted by the coronavirus.
March 18: President Trump announced: Temporary closure of the U.S.-Canada border to non-essential traffic. Plans to invoke the Defense Production Act in order to increase the number of necessary supplies needed to combat coronavirus. FEMA has been activated in every region at its highest level of response. The U.S. Navy will deploy USNS Comfort and USNS Mercy hospital ships. All foreclosures and evictions will be suspended for a period of time.
March 19: President Trump announced: Very encouraging progress shown by anti-malaria drug Hydroxychloroquine for fighting coronavirus. Carnival Cruise Lines will make ships available for use as hospitals in impacted areas to use for non-coronavirus patients.
March 19: The State Department issued a global level 4 health advisory, telling Americans to avoid all international travel due to coronavirus.
March 20: The U.S. and Mexico agree to mutually restrict nonessential cross-border traffic.
March 20: Secretary Mnuchin announced at the direction of President Trump that Tax Day will be moved from April 15 to July 15 for all taxpayers and businesses.
March 20: President Trump: Announced the CDC will invoke Title 42 to provide border patrol with tools to secure the borders.
March 20: Secretary Azar announced: The CDC is suspending all illegal entries to the country based on the public health threat, via Section 362 of the Public Health & Security Act.
March 22: President Trump announced: Governors will remain in command of National Guard forces & the federal govt will fund 100% of operations cost. He directed the federal govt to provide 4 large federal medical stations with 2,000 beds for CA & 1,000 beds for NY & WA.
March 22: FEMA issued guidance for tribal governments to seek federal assistance under the President’s emergency declaration.
March 23: President Trump signed an executive order invoking section 4512 of the Defense Production Act to prohibit the hoarding of vital medical supplies.
March 23: Attorney General Barr announced:
The Justice Department held a National Task Force meeting on hoarding and price gouging.
Each of the 93 U.S. Attorney General offices is designating a lead prosecutor to prevent hoarding.
March 23: The Treasury Department announced it is working with the Federal Reserve to lend up to $300 billion to businesses and local governments.
March 24: The U.S. Army issued orders for three army hospitals to deploy their health care professionals to New York and Washington state, at the direction of Secretary of the Army Ryan McCarthy.
March 26: President Trump held a phone call with Chinese President Xi Jinping to discuss the coronavirus.
March 27: President Trump signed The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act into law.
March 27: President Trump signed a Defense Production Act memorandum ordering General Motors (GM) “to accept, perform, and prioritize federal contractors for ventilators.
March 27: President Trump signed an executive order allowing the military to activate members of the Selected Reserve and Ready Reserve to active duty to assist with the Federal response to the coronavirus.
March 27: President Trump appointed Office of Trade and Manufacturing policy director Peter Navarro to serve as the Defense Production Act Policy Coordinator.
March 27: President Trump announced that Boeing offered the use of three “Dreamlifter” cargo air crafts to transport medical supplies across the country.
March 27: Partnering with FEMA, the CDC, and the Coronavirus Task Force, Apple released a coronavirus app which allows users to screen for their symptoms.
March 27: President Trump spoke with British Prime Minister Boris Johnson about the global coronavirus response and committed to helping provide ventilators to the U.K. where possible.
March 27: Emory University began enrolling participants for a phase one clinical trial, sponsored by the NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), of a new, potential coronavirus vaccine.
March 27: FEMA Administrator Pete Gaynor spoke to the director of each of the state’s emergency operations about the state-led, federally supported coronavirus response effort.
March 29: President Trump announced that CDC guidelines will be extended through April 30 to promote #socialdistancing and other measures to stop the spread of the #coronavirus.
March 29: President Trump met with supply chain distributors including FedEx, Cardinal Health, and UPS to discuss ways to get state and local governments necessary medical supplies to combat the coronavirus.
March 29: The first “Project Airbridge” shipment of medical supplies from abroad, organized by FEMA, landed at JFK airport, carrying 80 tons of masks, face shields, and other vital medical supplies.
March 29: President Trump announced that Cigna and Humana are waving co-pays for coronavirus treatment.
March 29: HHS accepted 30 million doses of Hydroxychloroquine, donated by Sandoz, and one million doses of Chloroquine, donated by Bayer Pharmaceuticals, for clinical trials and possible treatment of coronavirus patients.
March 30: Secretary Azar announced that the FDA has approved Battelle’s N95 mask sanitization process for use to decontaminate tens of thousands of masks per day.
March 30: President Trump announced further private sector commitments to manufacture personal protective equipment by MyPillow, Honeywell, Jockey, Procter & Gamble, and United Technologies.
March 30: President Trump announced: “more than 14,000” National Guard service members have been activated to respond to the coronavirus outbreak.
March 30: President Trump announced that in the coming days the Federal Government will be delivering: 400 ventilators to Michigan, 300 ventilators to New Jersey, 150 ventilators to Louisiana, 150 ventilators to Illinois, and 50 ventilators to Connecticut.
March 30: President Trump spoke to Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte of Italy and pledged to send $100 million of medical supplies to aid Italy’s battle against coronavirus.
March 30: Ford Motor Company committed to producing 50,000 ventilators in 100 days.
March 30: HHS took steps to accelerate a clinical trial of a potential coronavirus vaccine developed by Janssen Research & Development.
March 31: President Trump officially issued “30 Days to Slow the Spread” guidance to mitigate the outbreak of coronavirus.
March 31: President Trump participated in a conference call with executives of American Network Service Providers to promote connectivity amid social distancing.
March 31: President Trump announced that the Treasury Department and SBA are rapidly mobilizing money from the CARES Act’s $349 billion paycheck protection program, with the program set to be “up and running” by April 3.
March 31: President Trump announced the Army Corps of Engineers & FEMA will construct:
8 medical facilities.
March 31: Vice President Pence announced that 17,000 National Guard Servicemen have been activated across the country to assist in the coronavirus response.
March 31: The FDA issued an emergency use authorization for a two-minute coronavirus antibody test developed by Bodysphere Inc.
March 31: The Treasury Department and IRS launched the employee retention credit, created by the CARES Act to incentivize businesses to keep their employees on payroll, and said businesses can begin using it.
March 31: The VA announced that it had expanded virtual services to veterans.
April 1: The White House, HHS, and the FDA worked with Senator Rob Portman to acquire and authorize for use over two million gowns donated to the Strategic National Stockpile by Cardinal Health.
April 1: Dr. Birx announced that the White House issued a challenge to universities and states to develop ELISA, or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays, tests to detect coronavirus antibodies in larger communities more quickly.
April 1: The Treasury Department announced that Social Security recipients, including senior citizens, disabled Americans, and low-income Americans who do not file tax returns will have their coronavirus relief payments directly deposited into their bank accounts.
April 2: President Trump ordered the Federal Government to cover the costs of all National Guard operations in states with recently approved disaster declarations.
April 2: Secretary Mnuchin and Small Business Administrator Jovita Carranza announced the Paycheck Protection Program, created by the CARES Act to provide $350 billion in loans to small businesses, will be launched tomorrow.
April 2: Secretary Mnuchin announced that the first relief payments will be dispersed within two weeks.
April 2: Vice President Pence announced that all Blue Cross Blue Shield Members will be waiving out of pocket costs for coronavirus treatment.
April 2: Rear Adm. Polowczyk announced FEMA’s Supply Chain Stabilization Task Force has delivered: 27.1 million surgical masks; 19.5 million N95 respirator masks, 22.4 million surgical gloves; 5.2 million face shields; and Over 7,600 ventilators.
April 2: First Lady Melania Trump had a phone call with Mrs. Sophie Grégoire Trudeau of Canada, who is recovering from the coronavirus.
April 2: The Department of Justice and HHS distributed 192,000 N95 respirator masks confiscated from price gougers to health care workers in New York and New Jersey.
April 2: The FDA approved the first coronavirus antibody test, developed by Cellex.
April 2: HUD announced it was immediately making $3 billion of CARES Act funding available to help America’s low-income families and most vulnerable citizens across the nation.
April 2: The Energy Department announced it would immediately make 30 million barrels of the strategic petroleum reserve’s (SPR’s) oil storage capacity available to struggling U.S. oil producers.
April 3: President Trump announced new voluntary CDC guidelines that all Americans wear non-medical, fabric or cloth face masks to prevent asymptomatic spread of coronavirus.
April 3: The President met with energy execs from Phillips 66, Devon Energy, Continental Resources, Hilcorp Energy, Occidental Petroleum, The American Petroleum Institute, The Energy Transfer Partners, Chevron, and Exxon Mobil to discuss coronavirus’ impact on the energy industry.
April 3: President Trump spoke with French President Emmanuel Macron to discuss convening the five permanent members of the UN Security Council in an effort to defeat the coronavirus and discuss its impact on the world.
April 3: President Trump signed a Presidential Memorandum blocking the export of N95 and other respirator masks, surgical masks, PPE gloves, and surgical gloves to ensure they are available in the U.S. – designating them as “scarce” under the Defense Production Act.
April 3: President Trump announced that Anthem will waive co-pays for coronavirus treatment for 60 days.
April 3: President Trump announced that uninsured Americans will have their coronavirus treatment covered, using funding from the CARES Act.
April 3: Trump Administration officials spoke to the directors of the two largest health care providers in Louisiana, Ochsner and LCMC Health, to discuss their need for medical supplies.
April 3: President Trump directed FEMA to send Ochsner Surgical Gowns.
April 3: President Trump announced that 9,000 retired Army medical personnel have volunteered and are assisting the federal response to the coronavirus.
April 3: President Trump announced that the DOJ and HHS have together secured: 200,000 N95 masks; 130,000 surgical masks, and 600,000 gloves from hoarders and have distributed the supplies to health care workers.
April 3: Vice President Pence announced that 18,000 machines are already available across the country to administer Abbott 15 Minute Coronavirus Tests, with another 1,200 soon to be distributed to states.
April 3: Secretary Azar announced a public-private partnership with Oracle to collect crowd-sourced data on coronavirus therapeutic treatments.
April 3: The SBA launched the Paycheck Protection Program for small businesses impacted by the coronavirus pandemic, issuing more than 17,500 loans valued at $5.4 billion.
April 3: The Army Corps of Engineers is working with states to assess 750 requests for temporary hospital facilities, having completed 673 already.
April 3: The FDA announced it would coordinate the national effort to develop blood-related therapies for COVID-19.
April 3: The Defense Department’s Joint Acquisition Task Force launched a new portal giving the private sector the ability to submit information and solutions to the DOD.
April 3: The State Department announced that they have awarded contracts for 8 new medical facilities, totaling 9,693 new beds.
April 3: The Department of Labor issued guidance to help employers reduce their use of N95 respirators, freeing up supply for the coronavirus response.
April 3: HUD announced it is making $200 million in Indian housing block grants for Indian Tribes under the CARES Act.
April 3: EPA Administrator Wheeler held a call with retailers and marketplace platforms to discuss ways to protect consumers from fake disinfectants.
April 3: First Lady Melania Trump held a phone call with Mrs. Brigitte Macron of France to discuss the coronavirus response.
April 4: President Trump announced that 1,000 members of the Defense Department’s Medical Corps will be deployed to New York to assist in the fight against coronavirus.
April 4: President Trump spoke to commissioners of major league sports organizations including the MLB, NFL, & NBA, recognizing what the leagues, teams, and players are doing in their communities to combat coronavirus.
April 4: President Trump tweeted encouragement to American children unable to start their Little League baseball season on time due to coronavirus.
April 4: President Trump announced that he was considering a second coronavirus task force focused on the economy.
April 4: President Trump urged PM Modi of India to allow Hydroxychloroquine to be shipped to the United States.
April 4: President Trump announced that the U.S. government has repatriated over 40,000 Americans from 75 countries.
April 4: Vice President Pence spoke to Governors of New York, New Jersey, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Michigan, and Maryland.
April 5: President Trump announced that by Tuesday, 3,000 military and medical personnel will have deployed to New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut to assist in the coronavirus response effort.
April 5: President Trump announced that the Trump Administration will be sending New York 600,000 N95 masks tomorrow, including 200,000 to Suffolk County alone.
April 5: President Trump announced that the Administration will soon send: 300 ventilators to Michigan, 200 ventilators to Louisiana, 600 ventilators to Illinois, 100 ventilators to Massachusetts, and 500 ventilators to New Jersey.
April 5: President Trump announced the establishment of a federal coronavirus medical station in Washington D.C.
April 5: President Trump announced that Washington has returned 400 ventilators to the strategic national stockpile.
April 5: President Trump announced that the government has stockpiled 29 million doses of Hydroxychloroquine.
April 5: Adm. Polowczyk announced that three Project Airbridge flights of medical supplies landed across the U.S. today carrying: 1 million gowns; 2.8 million surgical masks; and 11.8 million gloves.
April 5: Adm. Polowczyk spoke to top health officials from states severely impacted by the coronavirus to discuss the supply chain.
April 5: Secretary Wilkie announced that the VA is making 1,500 beds available at VA hospitals to help states and localities across the country.
April 5: FEMA and The Army Corps of Engineers completed renovations at the McCormick Place Pavilion in Chicago, providing an additional 500 hospital beds for the city.
April 6: President Trump announced an agreement with 3M to produce and import 55.5 million N95 masks each month for the next three months.
April 6: President Trump held a call with CEOs from pharmaceutical and bio-tech companies to discuss potential coronavirus therapeutics.
April 6: President Trump approved Governor Murphy’s request to allow New Jersey patients aboard the USNS Comfort.
April 6: President Trump approved Governor Cuomo’s request to allow the treatment of coronavirus patients on the USNS Comfort.
April 6: President Trump announced that CVS will open two new drive-thru coronavirus testing sites in Georgia and Rhode Island. Both will use Abbott’s rapid coronavirus test.
April 6: President Trump announced that the FDA authorized Inovio’s potential coronavirus vaccine for a clinical trial, while 10 potential coronavirus therapeutic agents are in “active trials” with another 15 potential therapeutics in plans for clinical trials.
April 6: President Trump praised the work of the private sector, including Apple and Salesforce, who have agreed to donate personal protective equipment to help defeat the coronavirus.
April 6: President Trump announced that The Army Corps of Engineers is building 22 field hospitals and alternative care sites in 18 states.
April 6: President Trump announced that 8,450 hospital beds and 8,000 ventilators have been deployed across the country from federal stockpiles.
April 6: Vice President Pence announced that 21,000 National Guard Servicemen have been activated across the country to assist in the fight against coronavirus.
April 6: VP Pence announced that thanks to California’s donation of 500 ventilators, the federal government will send: 200 ventilators to Maryland, 100 ventilators to Delaware, 100 ventilators to Nevada, 50 ventilators to Washington DC, and 50 ventilators to Guam & the Northern Mariana Islands.
April 6: The CDC began publishing a new, data-centered coronavirus surveillance report on coronavirus.gov.
April 6: HHS announced an additional $186 million in CDC funding for state and local jurisdictions combatting the coronavirus.
April 6: HHS announced it will be purchasing 15-minute coronavirus tests from Abbott for state, territorial, and tribal lab, and for the Strategic National Stockpile.
April 6: The Department of Education announced a streamlined process making it easier for states to use federal education funding for distance learning during the coronavirus outbreak.
April 7: President Trump participated in a conference call with banking executives to discuss how to best deliver financial aid and technical assistance to small businesses.
April 7: President Trump announced the SBA has processed “more than $70 billion” in loans to help small businesses as part of the Paycheck Protection Program.
April 7: President Trump announced that in addition to the 8,675 ventilators in the strategic national stockpile, the federal government will be acquiring 110,000 ventilators in the next three months to be distributed to states in need.
April 7: President Trump announced his intent to ask Congress for an additional $250 billion for the Paycheck Protection Program to loan to small businesses.
April 7: Vice President Pence participated in a conference call with over 500 business owners to discuss their needs amid the coronavirus response effort.
April 7: CMS Administrator Verma announced that CMS will make available an additional $30 billion in grants this week for health care organizations with increased operating costs due to the coronavirus.
April 7: The Department of Transportation finalized a requirement that airlines who receive assistance under the CARES Act continue flights to destinations they were serving before the outbreak, ensuring commercial flights are available.
April 8: President Trump spoke to over 10,000 faith leaders & more than 3,000 state, local, and tribal officials to discuss the coronavirus response effort.
April 8: Under the DPA, HHS announced a $646.7M contract with Philips to produce 2,500 ventilators for the Strategic National Stockpile by the end of May, and a total of 43,000 by December.
April 8: President Trump thanked Indian PM Modi for allowing a shipment of the life-saving drug hydroxychloroquine to be released to the U.S.
April 8: Vice President Pence announced: $98B in forgivable loans were disbursed through the Paycheck Protection Program. 27,000 National Guard service members were activated across the country to assist in the coronavirus response
April 8: Customs and Borders Protection announced with FEMA that it will detain shipments of PPE in order to keep critical medical supplies within the U.S. for domestic use.
April 8: HHS announced an agreement with DuPont and FedEx to rapidly manufacture and deliver 2.25M new Tyvek Protective Suits to the Strategic National Stockpile over the next five weeks.
April 8: HHS expanded telehealth services for Native Americans through The Indian Health Service.
April 8: HHS awarded $1.3B from the CARES Act to 1,387 health centers in all 50 states, 8 territories, and the District of Columbia to fight coronavirus.
April 8: CMS issued updated guidance based on CDC guidelines to protect patients and health care workers in hospitals from the coronavirus.
April 8: The USDA announced its approval of Arizona’s & California’s request for food stamp recipients to purchase food online, allowing these recipients to purchase groceries for delivery.
April 8: The VA announced that it has begun using funding from the CARES Act to pay overtime, hire new staff, and purchase supplies including PPE, beds, and pharmaceuticals.
April 9: President Trump spoke with mental health advocates from across the country to discuss their work amid the coronavirus outbreak.
April 9: President Trump announced that there are currently 19 potential coronavirus therapies being tested and another 26 potential therapies in active planning for clinical trials.
April 9: Vice President Pence announced that $125B in Paycheck Protection Program forgivable loans has been approved to date.
April 9: Vice President Pence announced that a total of 29,000 National Guard service members have been activated across the country to assist in the coronavirus response.
April 9: Vice President Pence announced that to date 4,100 military medical personnel have been deployed to New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut.
April 9: The Treasury Department announced that it extended over 300 tax filing, payment, and administrative deadlines to give relief to taxpayers.
April 9: Working with the Treasury Department, the Federal Reserve announced new lending programs providing up to $2.3T in loans to businesses and state & local governments.
April 9: HHS announced it would relax enforcement of HIPPAA for pharmacies and other organizations that are working at coronavirus testing sites, helping these groups focus on testing.
April 9: Secretary of Education DeVos announced that $6.3B in CARES Act funding will be immediately distributed to colleges and universities to provide cash grants to students affected by the coronavirus.
April 9: Secretary of Education DeVos announced that $6.3B in CARES Act funding will be immediately distributed to colleges and universities to provide cash grants to students affected by the coronavirus
April 9: The EPA announced that more than 11,500 pieces of PPE have been transferred to FEMA, which will be later transferred to state and local agencies across New England combating the coronavirus.
April 9: The USDA launched the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT) Program in Michigan, which will help feed children eligible for USDA school lunch programs who are now home during the coronavirus outbreak.
April 9: The USDA announced relief for farmers across the country by giving borrowers 12 months to repay marketing assistance loans (MAL), helping protect farmers from being forced to sell crops to make loan payments.
April 9: CMS temporarily suspended a number of regulations so that hospitals, clinics, and other health care providers can book the number of staff to confront the coronavirus
April 10: President Trump announced that 60 mask sterilization systems, with the ability to clean over 80,000 masks approximately 20 times, will be sent to 10 cities.
April 10: President Trump spoke with Russian President Vladimir Putin to discuss the global coronavirus response and the global energy market.
April 10: President Trump announced that a field hospital in Seattle will be leaving, as Washington State’s coronavirus outbreak becomes more manageable.
April 10: President Trump announced that his administration is working to bring blood-based serology tests to market “as quickly as possible” so Americans can determine if they have had the coronavirus.
April 10: President Trump announced that he will be establishing an “Opening Our Country Council” with more details coming early next week.
April 10: President Trump signed a Presidential Memorandum to facilitate the supply of medical equipment and other humanitarian relief to Italy.
April 10: Dr. Fauci spoke to Arkansas Governor Asa Hutchinson and Wyoming Governor Mark Gordon to discuss coronavirus mitigation in those states.
April 10: Vice President Pence, CDC Director Redfield, & Surgeon General Adams spoke to over 400 leaders of the African American community, including Jesse Jackson, NAACP representatives, & the National Black Nurses Association to discuss the impact of the coronavirus.
April 10: Vice President Pence announced that: 29,600 National Guard Troops have been activated. 4,700 active duty medical personnel have been deployed to nine states.
April 10: HHS began delivering $30B in relief funding to health care providers, part of the $100B allocated to health care providers by the CARES Act.
April 10: The Treasury Department launched a web portal to help Americans who did not file tax returns receive their coronavirus relief payments under the CARES Act.
April 10: The Treasury Department announced it will launch a new “get my payment” app where Americans can enter their direct deposit information to get coronavirus relief payments quicker.
April 11: CMS expanded the requirements that private health insurers provide free coronavirus testing, saying that this includes anti-body testing and costs related to coronavirus testing, like emergency room or urgent care visits.
April 12: A deal brokered by President Trump was announced between The OPEC countries, Russia, and the U.S. to cut production and stabilize the oil market amid dual disruptions from coronavirus and the price war between Saudi Arabia & Russia.
April 12: The FDA issued an emergency authorization to devices from Advanced Sterilization Products, which can decontaminate approximately 4 million N95 respirators each day.
April 12: The FBI uncovered an international fraud scheme related to the attempted purchase of 39 million N95 masks by a Service Employees International Union Affiliate.
April 13: President Trump announced that new coronavirus infection rates remained “flat” over the weekend across the country.
April 13: President Trump announced that HHS is signing five new contracts for ventilators with GE, Hillrom, Medtronic, ResMed, & Vyaire, which will be added to the Strategic National Stockpile.
April 13: Dr. Fauci participated in a meeting with members of the Congressional Black Caucus to discuss the impact of the coronavirus on the African American community.
April 13: The U.S. government now has 28 million doses of hydroxychloroquine stockpiled.
April 13: The Treasury Department announced that 80 million Americans will receive economic impact payments in their bank accounts within the week.
April 13: The Treasury Department launched a new web portal which will quickly deliver CARES Act funding to state, local, and tribal governments.
April 13: The USDA released a “one-stop-shop” resource guide to help farmers, rural communities, and others know what resources and assistance are available to them as a response to the coronavirus.
April 13: The USDA approved Rhode Island’s request to join the Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT) Program, which will help feed children eligible for USDA school lunch programs who are now at home during the coronavirus outbreak.
April 13: The Department of Commerce and Census Bureau announced adjustments to the 2020 Census operational schedule to protect census workers and the American people during the coronavirus outbreak.
April 13: The VA announced a “dramatic” increase in virtual and tele-mental health appointments, a sign that veterans are still able to access care remotely during the coronavirus.
April 13: The DHS announced it had processed more than 271,000 travelers through enhanced screenings at airports as of April 12, referring nearly 1,500 to the CDC for further evaluation.
April 14: President Trump spoke with French President Emmanuel Macron to discuss the global coronavirus response and the re-opening of the global economy.
April 14: President Trump extended an order for the federal government to cover the costs of all National Guard operations to states with recently approved disaster declarations.
April 14: HHS announced it was distributing the $3.5 billion in childcare and development block grant funding included in the CARES act.
April 14: FEMA confirmed it send out 19.1 million doses of hydroxychloroquine to cities across the country.
April 14: More than 30,000 National Guard troops total have been activated to assist in the coronavirus response.
April 14: The Transportation Department announced $10 billion in relief for America’s airports from the Trump Administration’s newly created CARES Act airport grant program.
April 14: The Department of Education Announced $3 billion in education block grants for states to help schools, students, and educators at all levels.
April 15: HHS awarded $90 million to Ryan White HIV/AID Program recipients to combat coronavirus.
April 15: The Treasury Department launched the “Get My Payment” web app, allowing taxpayers to submit their direct deposit information online for their Coronavirus Economic Impact Payments.
April 15: The Treasury Department announced that supplemental security income recipients will receive their coronavirus relief payments as they would their SSI benefits, directly into their bank accounts or by debit cards or by check.
April 16: President Trump announced new, phased “opening up America again” guidelines.
April 16: President Trump participated in a video conference with leaders of the G7 to discuss a coordinated response to coronavirus, including pooling data and research, preparations to re-open their economies, and the WHO’s response to the coronavirus.
April 16: President Trump spoke with Republican and Democrat members of the Opening Up America Again Congressional Group on the coronavirus response and efforts to re-open the economy.
April 16: President Trump held a “Thank God For Truckers” ceremony on the South Lawn to thank truckers for moving goods and ensuring a stable supply of food, medical equipment, and other supplies during the pandemic.
April 16: President Trump reiterated his request for an additional $250 billion to replenish the paycheck protection program to help struggling small businesses.
April 16: President Trump announced that 4,000 community banks have participated in the paycheck protection program.
April 16: Under the DPA, HHS announced a $336 million contract with GE for 50,000 ventilators to be produced by July 13; in total, HHS has signed contracts for 41,000 ventilators by May and over 187,000 ventilators by the end of the year.
April 16: Secretary Mnuchin and Administrator Carranza urged Congress to provide additional funds to the paycheck protection program to help small businesses.
April 16: USAID announced that it committed nearly $508 million in emergency health, humanitarian, and economic aid around the world to help respond to the coronavirus pandemic.
April 16: The FDA encouraged Americans who have recovered from coronavirus to donate their plasma for the development of new treatments and therapies.
April 16: OSHA issued an alert, listing safety tips employers can follow to help keep manufacturing workers safe during the coronavirus pandemic.
April 17: President Trump and Secretary Perdue announced a $19 billion relief package for ranchers and farmers impacted by the coronavirus.
April 17: President Trump approved a major disaster declaration for American Samoa related to the coronavirus outbreak, meaning major disaster declarations have been approved in all 50 states and in all US territories for the first time in history.
April 17: President Trump participated in a conversation with faith leaders to discuss the coronavirus response and “express his eagerness to get” houses of worship reopened as soon as possible.
April 17: President Trump spoke to President Andrés Manuel López Obrador of Mexico to discuss Mexico’s need for additional ventilators.
April 17: Vice President Pence announced that a total of 33,000 National Guard troops and 5,500 active duty servicemembers have been activated to date to assist in the coronavirus response.
April 17: At the direction of FEMA, GM announced that they delivered the first GM-Ventec ventilators to Chicagoland hospitals.
April 17: To support FEMA’s Project Airbridge, UPS announced it would add over 200 flights in April.
April 17: The Treasury Department and VA announced that veterans who had not filed tax returns would automatically receive economic impact payments without additional paperwork.
April 17: The DOJ filed an injunction to halt the online sale of a supposed “miracle” treatment for the coronavirus which is “unapproved, unproven, and potentially dangerous”.
April 18: President Trump offered to send ventilators to Iran, if the Iranian government accepted the assistance.
April 18: President Trump consulted with FEMA and military officials about the coronavirus response.
April 18: President Trump spoke to the leaders of Poland, South Korea, and Bahrain about the global response to the coronavirus.
April 19: President Trump announced that 4.18 million coronavirus tests have been completed to date – more tests than France, The U.K., South Korea, Japan, Singapore, India, Austria, Australia, Sweden, and Canada combined.
April 19: 64 Project Airbridge flights have been completed to date carrying over 600 million pieces of gloves, gowns, and other PPE, with 50 additional flights scheduled in the future.
April 20: President Trump announced that HHS has distributed the $30 billion in relief funding to health care providers under the CARES act.
April 20: President Trump announced that there are currently 72 active trials for coronavirus therapies, with 211 additional therapies in the planning stages for active trials.
April 20: Vice President Pence announced that all DoD and federal labs will be made available for states to use in order to increase testing capacity.
April 20: Vice President Pence and Adm. Giroir announced that current testing capacity means that all 50 states are “ready right now to enter phase one” if they meet other criteria of the President’s Opening Up America guidelines.
April 20: Vice President Pence announced that the CDC is deploying teams of 10-12 experts to all states and territories to assist in contact tracing.
April 20: HHS’ substance abuse and mental health services administration (SAMHSA) announced $110 million in emergency grants for those suffering from mental illness and substance abuse amid the coronavirus pandemic.
April 20: The Defense Department announced the U.S. will be providing humanitarian support and relief to Italy, including transportation, supplies, and telemedicine.
April 20: Acting DHS Secretary Wolf announced that U.S., Canada, and Mexico had extended non-essential travel restrictions for an additional 30 days.
April 20: The Justice Department announced it cleared antitrust barriers which could have blocked the drug distribution company AmerisourceBergen from distributing medicine and supplies as part of the coronavirus response, including hydroxychloroquine.
April 20: The USDA approved Arizona and Illinois to join the pandemic EBT program, which will help feed children eligible for USDA school lunch programs in these states who are now at home during the coronavirus outbreak.
April 21: After negotiations with the Trump Administration, the Senate passed the Paycheck Protection Program and Health Care Enhancement Act, which includes an additional $382B for the PPP, $75B for hospitals, and $25B for coronavirus testing efforts.
April 21: President Trump announced that the FDA has now authorized more than 50 coronavirus diagnostic tests and four antibody tests.
April 21: HHS announced $995 million in CARES Act grants for older adults and the disabled.
April 21: The FDA issued an emergency approval for the first coronavirus test where a sample can be collected at home.
April 21: The State Department announced it is coordinating international humanitarian assistance with pacific nations including Australia, New Zealand, Japan, and Taiwan.
April 21: The USDA announced the states of Kentucky, Missouri, and Texas have been added to the SNAP online program, allowing food stamp recipients to purchase food online. The SNAP online pilot is currently operational in Alabama, Iowa, Nebraska, New York, North Carolina, Oregon, Washington State, and West Virginia. Maryland and New Jersey remain non‐operational pilot states.
April 21: Education Secretary DeVos announced an additional $6.2 billion in grants is available for universities to continue providing educational services during the outbreak, such as distance and remote learning programs.