
Mega Doctor News
Newswise — Scientists studied the brain activity of school-aged children during development and found that regions that activated upon seeing limbs (hands, legs, etc.) subsequently activated upon seeing faces or words when the children grew older. The research, by scientists at Stanford University, Palo Alto, California, reveals new insights about vision development in the brain and could help inform prevention and treatment strategies for learning disorders. The study was funded by the National Eye Institute and is published in Nature Human Behaviour.
“Our study addresses how experiences, such as learning to read, shape the developing brain,” said Kalanit Grill-Spector, Ph.D., a professor at Stanford University’s Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute. “Further, it sheds light on the initial functional role of brain regions that later in development process written words, before they support this important skill of reading.”
Grill-Spector’s team used functional MRI to study areas in the ventral temporal cortex (VTC) that are stimulated by the recognition of images. About 30 children, ages 5 to 12 at their first MRI, participated in the study. While in the MRI scanner, the children viewed images from 10 different categories, including words, body parts, faces, objects, and places. The researchers mapped areas of VTC that exhibited stimulation and measured how they changed in intensity and volume on the children’s subsequent MRI tests over the next one to five years.
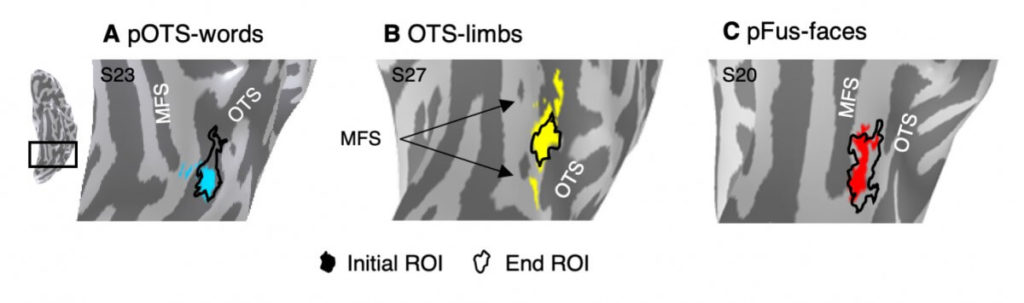
Results showed that VTC regions corresponding to face and word recognition increased with age. Compared to the 5-9-year-olds, teenagers had twice the volume of the word-selective region in VTC. Notably, as word-selective VTC volume doubled, limb-selective volume in the same region halved. According to the investigators, the decrease in limb-selectivity is directly linked to the increase in word- and face-selectivity, providing the first evidence for cortical recycling during childhood development.
“The loss of limb-selective volume surprised us,” said first author Marisa Nordt, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in Grill-Spector’s lab. “This challenges a theory of cortical development, which states that new representations, like emerging regions involved in word recognition, are sculpted on previously uncommitted cortex. Our study suggests that during childhood, cortical selectivity can change from one category to another.”
The study authors suggest that cortical recycling in VTC likely reflects adjustments to changing visual demands during childhood. For example, infants tend to look at faces. As they grow into toddlers and learn language, they are exploring objects and deciphering gestures. Word recognition becomes increasingly important as children learn to read.
In future studies, Grill-Spector and colleagues will explore whether decreases in limb-selective VTC volume have behavioral implications, asking if deviations from observed trends have bearing on development disorders.









