Mega Doctor News
Newswise — LOS ALAMOS, N.M., — A research team from Los Alamos National Laboratory and Purdue University have developed bio-inks for biosensors that could help localize critical regions in tissues and organs during surgical operations.
“The ink used in the biosensors is biocompatible and provides a user-friendly design with excellent workable time frames of more than one day,” said Kwan-Soo Lee, of Los Alamos’ Chemical Diagnostics and Engineering group.
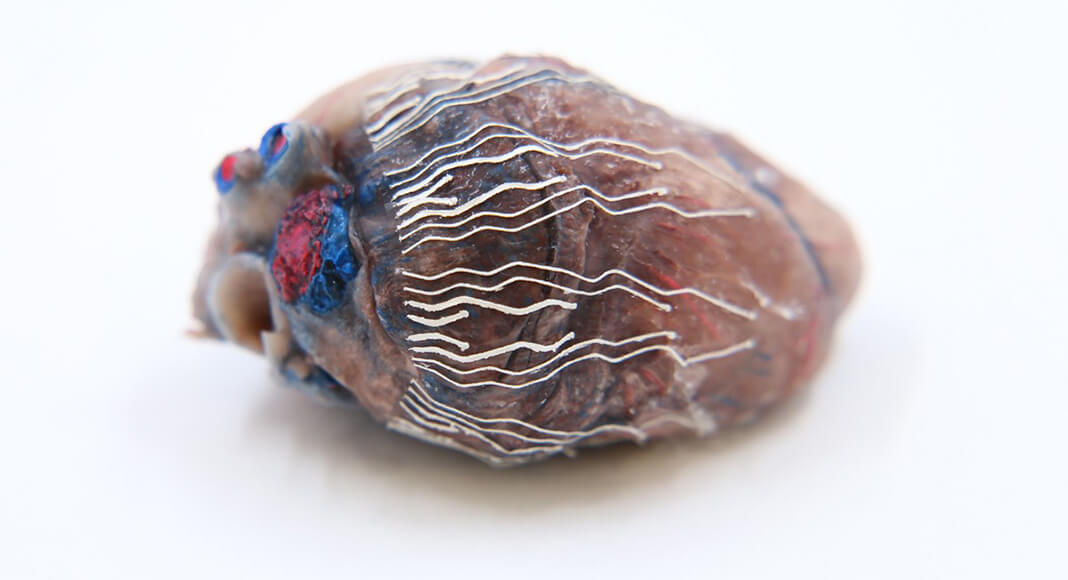
The new biosensors allow for simultaneous recording and imaging of tissues and organs during surgical procedures.
“Simultaneous recording and imaging could be useful during heart surgery in localizing critical regions and guiding surgical interventions such as a procedure for restoring normal heart rhythms,” said Chi Hwan Lee, the Leslie A. Geddes Assistant Professor of Biomedical Engineering and Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering and, by courtesy, of Materials Engineering at Purdue University.
Los Alamos was responsible for formulating and synthesizing the bio-inks, with the goal of creating create an ultra-soft, thin and stretchable material for biosensors that is capable of seamlessly interfacing with the surface of organs. They did this using 3D-printing techniques.
“Silicone materials are liquid and flow like honey, which is why it is very challenging to 3D-print without sagging and flowing issues during printing,” Kwan-Soo Lee said. “It is very exciting to have found a way to create printed inks that do not have any shape deformation during the curing process.”
The bio-inks are softer than tissue, stretch without experiencing sensor degradation, and have reliable natural adhesion to the wet surface of organs without needing additional adhesives.
Craig Goergen, the Leslie A. Geddes Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Purdue University, aided with the in vivo assessment of the patch via testing in both mice and pigs. The results showed the biosensor was able to reliably measure electrical signal while not impairing cardiac function.
The research was published in Nature Communications. It was funded by Science Campaign 2.









