Mega Doctor News
Newswise — New Brunswick, N.J. – A Rutgers-led team of researchers has developed a microchip that can measure stress hormones in real time from a drop of blood.
The study appears in the journal Science Advances.
Cortisol and other stress hormones regulate many aspects of our physical and mental health, including sleep quality. High levels of cortisol can result in poor sleep, which increases stress that can contribute to panic attacks, heart attacks and other ailments.
Currently, measuring cortisol takes costly and cumbersome laboratory setups, so the Rutgers-led team looked for a way to monitor its natural fluctuations in daily life and provide patients with feedback that allows them to receive the right treatment at the right time.
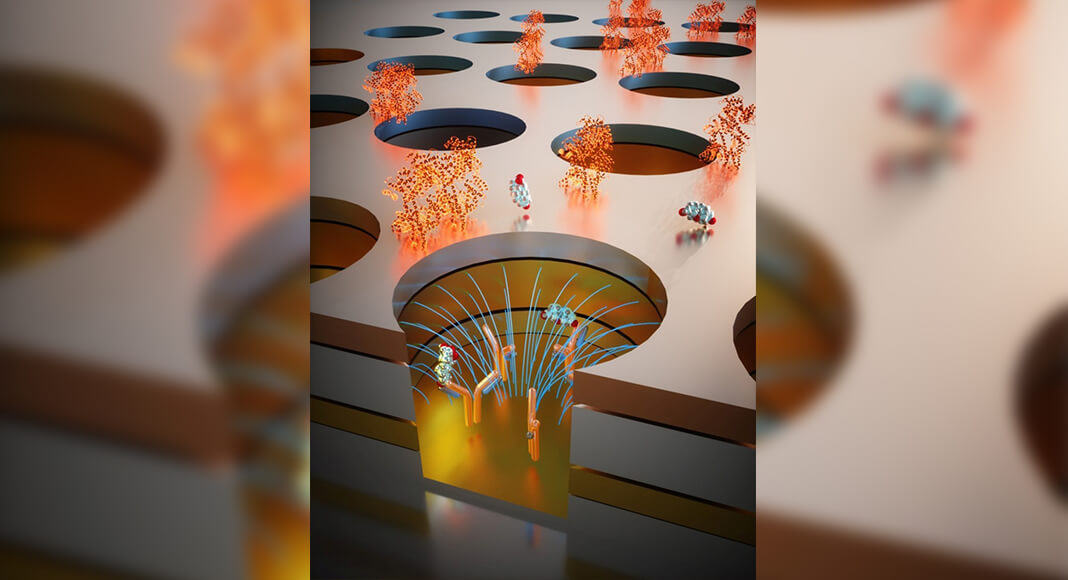
The researchers used the same technologies used to fabricate computer chips to build sensors thinner than a human hair that can detect biomolecules at low levels. They validated the miniaturized device’s performance on 65 blood samples from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
“The use of nanosensors allowed us to detect cortisol molecules directly without the need for any other molecules or particles to act as labels,” said lead author Reza Mahmoodi, a postdoctoral scholar in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Rutgers University-New Brunswick.
With technologies like the team’s new microchip, patients can monitor their hormone levels and better manage chronic inflammation, stress and other conditions at a lower cost, said senior author Mehdi Javanmard, an associate professor in Rutgers’ Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
“Our new sensor produces an accurate and reliable response that allows a continuous readout of cortisol levels for real-time analysis,” he added. “It has great potential to be adapted to non-invasive cortisol measurement in other fluids such as saliva and urine. The fact that molecular labels are not required eliminates the need for large bulky instruments like optical microscopes and plate readers, making the readout instrumentation something you can measure ultimately in a small pocket-sized box or even fit onto a wristband one day.” The study included Rutgers co-author Pengfei Xie, a Ph.D. student, and researchers from the University of Minnesota and University of Pennsylvania. The research was funded by the DARPA ElectRX program.








